Nazareth University Collaborates with Virtual Internships to Bolster Global Internship Access
Nazareth University partners with Virtual Internships to expand global work opportunities for students, providing valuable international experience.
It’s no longer if there will be a recession – rather, when. According to research firm, Ned Davis, there’s a 98% chance of a global recession, “which brings some sobering historical credibility to the table,” (CNN). The unfortunate damages of the looming recession have already caused more than 52,000 workers in the U.S. tech sector to lose their jobs in 2022 (Crunchbase News). These figures do not account for the recent mass layoffs amongst Stripe, Lyft, Chime, and Twitter that occurred in early November.
On a global scale, the unemployment rate decreased to 6.18% since the previous year, and the graph below demonstrates the highest youth unemployment rates across the EU from January 2022 (Statista).
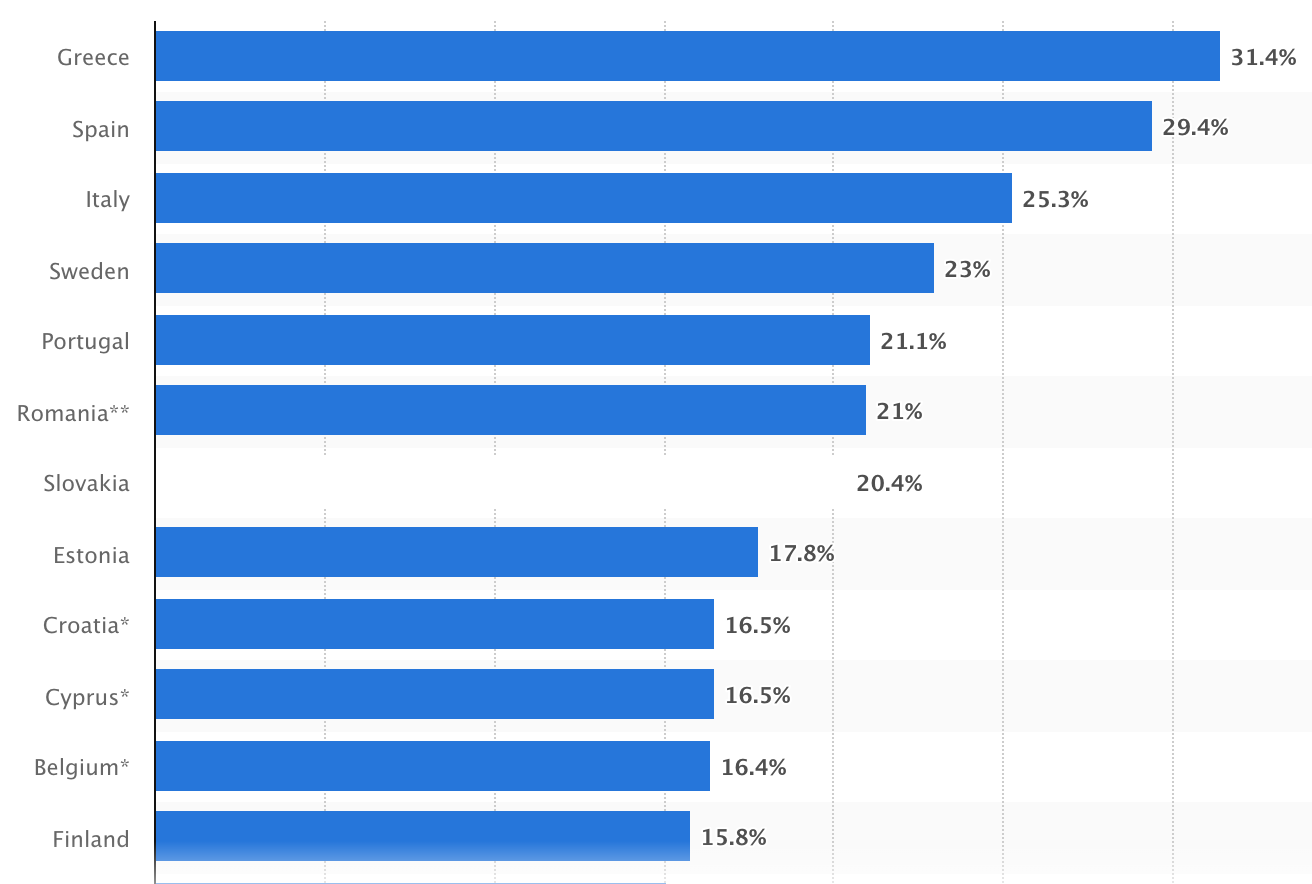
Youth unemployment rates in the EU, Statista 2022
The education industry is at its most competitive, and global instability has produced graduating students with limited options. Difficult circumstances are an opportunity for universities to innovate and invest in more strategic efforts, as was witnessed during the global pandemic.
COVID-19 has caused countless educational shifts, which were developed and deployed within weeks of the global lockdown. In November 2021, McKinsey surveyed 600 faculty members and 800 students from various universities in the United States and found more than 60% of students reported the classroom learning technologies they’ve used since COVID-19 began had improved their learning and grades (McKinsey). It is vital to maintain the momentum and positivity that digital breakthroughs have brought to education, especially during difficult times.
If a virtual employability program is not currently in place at the university setting, this is the best opportunity to innovate and utilize the power of technology to drive forward strategies to lead the digitization of higher education – because remote work is here to stay. Jennifer Shapely, LinkedIn’s Vice President of Global Talent Acquisition, “expects flexibility to remain a top priority for workers,” adding that she expects both work-life balance and flexible work arrangements to be “top talent drivers for the next couple of years,” (CNBC).
Taking into consideration the university strategic plans across universities and the European Commission, this paper focuses on three areas in which remote work-integrated learning programs can be instrumental in combating the impending global recession: Economic and Environmental Sustainability, International Cooperation, and Leadership in Innovation.
Each year, thousands of graduates enter the job market, but many of them lack practical work experience to help them secure a job. Companies want to hire job-ready graduates with technical know-how and the necessary soft skills to navigate the workplace.
Alongside the rise in remote working, online industry-led learning programs are becoming increasingly popular. They allow students to access work experience opportunities irrespective of where they live. Such internships improve accessibility for students who would otherwise be excluded from placements like these, such as international students, those on rural campuses, or others in countries with limited opportunities.
Remote work-based learning can bridge the gap between the university setting and the workforce by providing students with the digital competency, global literacy, and professional etiquette required to become competitive in the interconnected job market. Remote interns not only complete work online, perhaps utilizing software that is new to them, but they learn about the nuances of working on a global team, which leads to organic career readiness competencies, including: professionalism, technology, and teamwork (NACE).
Beyond personal wellbeing, remote work has had a positive effect on the environment as well. Remote workers have a zero commute, incidentally lowering their carbon footprint. Kevin Rockman, a Professor of Management at George Mason University’s School of Business, points out that although there are undeniable downsides to a solitude environment, “there is no doubt that wellbeing is stronger given remote work … trading commuting time for personal health, family or recreation is almost guaranteed to bring positive benefits” (BBC).
When most businesses shifted to remote work in 2020, carbon dioxide emissions from transportation were reduced by 15%
Eradicated commute times and increased flexible work hours, allows remote workers to have better work/life balance which increases productivity.
The pandemic has pushed universities to seek collaborations in order to survive during this uncertain political, economical, and ecological climate. Underrepresented and marginalized populations that have had difficulties accessing global opportunities now have the opportunity to accelerate their career and provide stability to their lives in their home countries.
With real-world, online work experience placements students get a great opportunity to experience a virtual workplace, build their power skills, get tailored support and mentoring, and grow their networks from their home country.
“The internship program has given me the opportunity to be a part of our global working community, and to be honest, without this internship, it could’ve taken me years, and a lot of missed opportunities to learn what I did in only two months with Virtual Internships.”
This is just one testimonial of an underserved student achieving the same quality and access as their more privileged peers – who do not experience the same inequalities. Consider the factors of implementing a Virtual Internship program to make this experience accessible to a wider population. Offering hybrid or fully-remote work-integrated learning programs will open doors for students who are unable to find employment in their home countries or who simply cannot afford to travel.
More than ever, it is time to weigh the added values of virtual collaborations on the same scale as in-person experiences and learn the benefits of this new mode of work. Career and global education administrators at all levels of the university must turn their competition into complementation, teaming with other like-minded partners in order to provide students with vast professional development opportunities worldwide.
Keep in mind that the world won’t always be in a recession. When the economy bounces back, will universities be ready and have a strong offering of academic programs that builds trust amongst GenZ cohorts? Hint: they don’t trust us (Inside HigherEd). If online work experience programs are halted in a competitive labor market, universities could miss out on an opportunity to be the leaders by guaranteeing internship placements that are perfectly suited based on the students’ career interests, passions, and experiences.
The economy is unpredictable. But universities are not powerless in a recession. If the higher education system can lean into flexible online learning, and introduce stackable credentials and certification programs, they might discover a whole new population to engage and enroll, mitigating the impact of economic downturns.
This is particularly true, for example, for Botho University, whose mission is to produce well-rounded, entrepreneurial, and globally-employable graduates. In order to achieve this mission, they partnered with Virtual Internships to design a credit-bearing, mandatory semester-long placement module in all academic programs to provide students with practical work experience (The sustainable path to global employability).
“At the end of the day, virtual internships have helped our students overcome geographical barriers and work with international employers and multicultural teams, something we have been trying for a few years now. We can now emphatically say with evidence that we are building a global workforce and we see this as a moment of tremendous opportunity. The feedback from the virtual interns has been very fulfilling and validates our decision to invest in virtual internships.”
The looming recession cannot be prevented, as the economic cycle must follow its due course. However, there are ways in which to effectively plan ahead during a time of conservative spending and distrust in the market.
By investing in online experiential learning, or a hybrid model that allows both in-person and virtual experiences, the impending increase of unemployment rates can be reduced.
Remote experiential learning is a solution not only for students and universities but the environment as well. Remote work provides further career exploration across cultures while cutting down CO2 emissions.
Remote work is not a trend, but a new lifestyle that universities must integrate within their pedagogy. The benefits will aid students in achieving their professional/personal goals, and improve the ROI for universities that are now competing with agile bootcamps that offer shorter, cheaper, customizable, and remote options. Universities have gained international notoriety for their innovation in adapting to remote work and the necessary preparation necessary to be competitive in the global marketplace.
The global pandemic has proven that higher education institutions can work quickly during unpredictable times. A global recession is predicted, the time to take action is now.
Nazareth University partners with Virtual Internships to expand global work opportunities for students, providing valuable international experience.
What are the best internships for college students? How can a student earn credit for their internship and why is this a good option?
Virtual Internships knows the importance of ROI for university students and has created an opportunity to gain academic credit for internships.