Traditional degrees alone may no longer guarantee coveted graduate job opportunities in this evolving job landscape. In fact, a staggering 56% of Americans now question the value of a four-year education in terms of time, cost, and effort. This paradigm shift is forcing universities and educational providers to reevaluate their academic offerings, giving rise to the concept of experiential learning.
Experiential learning takes on diverse forms, from simulated experiences and micro-learning to immersive case studies and standard internships. But which among these diverse avenues holds the key to preparing students for the future of work? Here, we dive into the advantages and disadvantages of each, shedding light on the path forward in the realm of education and career readiness.
4 Key Elements of Work-Based Learning Experience
In this case, we’re going to use different types of internships as the key example of work-based learning. There are many different internship models but here we are going to explore, the key elements that make up a meaningful experience before diving into each type.
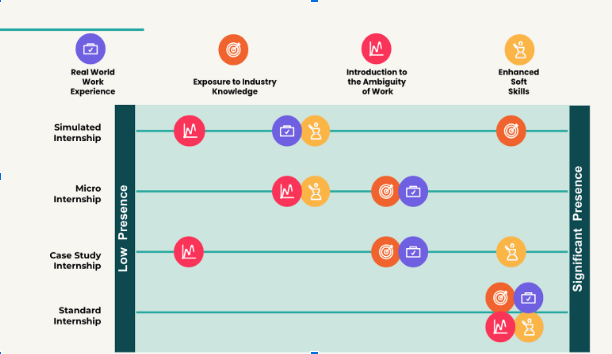
- Real-world work experience: Providing students with exposure to authentic work environments and challenges.
- Exposure to industry knowledge: Offering insights into specific industries, helping learners gain a deeper understanding of their chosen fields.
- Introduction to the ambiguity of work: Familiarizing students with the uncertainties and complexities they will encounter in real-world work settings.
- Enhanced soft skills: Developing crucial interpersonal and problem-solving skills that are highly sought after in the job market.
Simulated Internship or Job Simulation
Simulated internships or job simulations are designed as recruitment and assessment tools. These programs replicate real-world job tasks to assess a candidate's skills and suitability for a specific role. They come in various forms, including hands-on tasks, virtual simulations, role-playing, and multi-step challenges.
For instance, the Forage program offers students the opportunity to engage in 4-6 hour mini projects that provide a glimpse into the workings of a company. This exposure enhances their industry knowledge and allows them to showcase their skills. However, these simulated internships may lack opportunities for students to build professional networks and offer limited exposure to real workplaces and soft skill development due to their short and narrow scope. Additionally, projects are often completed by a large number of participants within a short timeframe, resulting in limited feedback for skills and personal development.
Micro Internship
Micro internships, characterized by their brevity, offer short-term, project-based experiences in the professional world. They are designed to provide students with practical insights and skills, making them suitable for those with tight schedules.
Platforms like Parker Dewey offer students the chance to engage in short-term projects, typically lasting 4-6 hours. While these internships offer real-world exposure and industry knowledge, the brevity limits the depth of the experience. Micro internships also lack the introduction to the ambiguity of work and the opportunity to enhance soft skills often associated with longer experiential learning programs.
Case Study Internship
Case study internships immerse students in real-world scenarios within professional contexts, allowing them to apply theoretical knowledge to practical problem-solving. These programs contribute significantly to the development of soft skills.
Platforms like Riipen and Practera collaborate with faculty and universities to match learners with consulting and industry-led experiences. However, the structured nature of case study internships may limit the ambiguities found in real-world settings and offer only a modest exposure to industry insights and actual work experiences.
Standard Internships
Standard internships are traditional on-the-job training experiences for white-collar and professional careers, varying in length from a few weeks to several months. Platforms like Virtual Internships offer standard internship programs in a remote setting, providing accessibility to a diverse range of learners.
One notable feature of standard internships is the exposure to industry knowledge under the guidance of experts. Learners often work with experienced professionals, set learning objectives, and acquire practical skills while expanding their professional network. These internships offer opportunities for lifelong learners to embrace the ambiguity of the workplace, gain industry-specific insights, acquire power skills, and experience the real world firsthand.
Support Your Student’s Career Development with Meaningful Work Experience
Incorporating experiential learning into your academic curriculum is a strategic move to prepare your students for the future of work. These opportunities allow universities to align placement programs with students' learning objectives, ensuring a comprehensive preparation for the dynamic world of work.
Choosing the right work-based learning program may seem daunting, but it's crucial to make informed decisions. Our partners, such as the University of the People, Purdue University, and Bridgewater State University, have successfully integrated remote standard internship programs into their academic curriculum, benefiting students who face barriers to work experience due to work, location, and other commitments.
Virtual Internships stands out with our commitment to providing impactful outcomes. With a focus on guaranteed student placement in their chosen career field, our innovative platform offers standard internships that can be executed and supervised remotely. By providing standard internships, we ensure that participants gain real-world work experience, exposure to industry knowledge, an introduction to the ambiguity of work, and enhanced soft skills—a crucial preparation for the emerging professional world infused with technology and AI.
